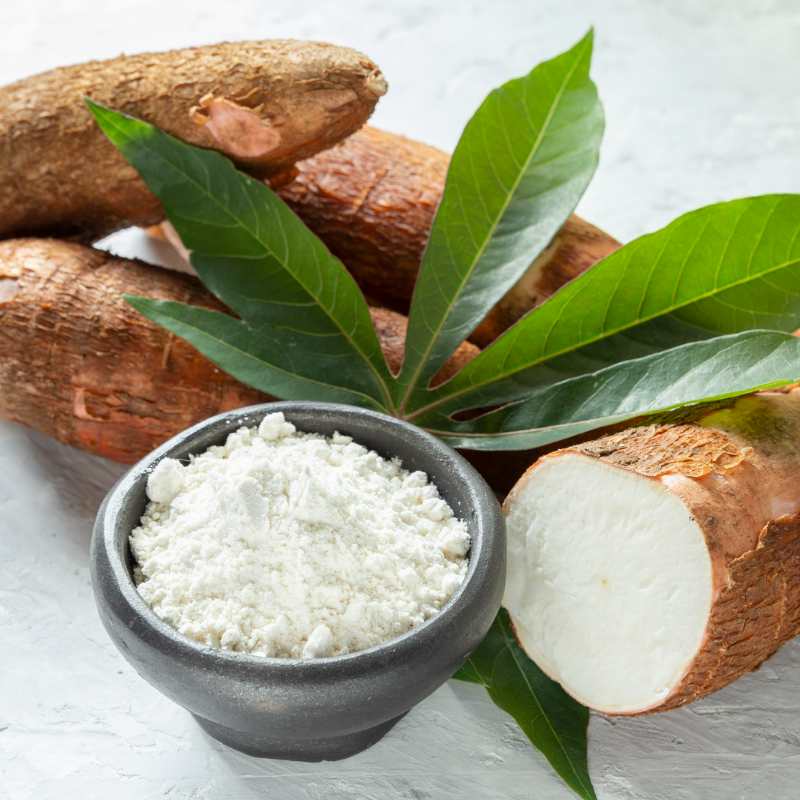
Tapioca starch, a fundamental component of countless food products and industrial applications, is more than just a kitchen staple. This article delves into the chemistry of tapioca starch, exploring its molecular structure, production process, and the wide range of applications that make it a critical player in various industries.
The Molecular Makeup
Tapioca starch, like other starches, is a complex carbohydrate composed of glucose units linked together. Its molecular structure resembles a branching chain, where the glucose molecules are connected through alpha (α) and beta (β) linkages. This structural arrangement makes tapioca starch an ideal source of readily available energy when broken down through digestion.
Extraction and Processing
The journey of tapioca starch begins with the cassava root (Manihot esculenta), a drought-tolerant plant native to South America. The starch is extracted through a multi-step process:
Harvesting: Cassava roots are harvested and cleaned to remove soil and impurities.
Grating: The cleaned roots are grated into a pulp.
Washing: The grated pulp is washed to separate the starchy granules from the fiber.
Settling: The starchy suspension is left to settle, allowing the heavier starch granules to sink.
Drying: The settled starch is dried to remove excess moisture.
Milling: The dried starch is milled into a fine powder, resulting in the familiar tapioca starch.
Chemical Properties
Tapioca starch is known for its unique chemical properties:
Neutral Flavor: It has a neutral taste, making it an ideal thickening agent in a wide range of culinary applications without altering the flavor of the dishes.
High Viscosity: Tapioca starch has a high viscosity, which means it forms a thick, smooth consistency when mixed with liquids.
Gelling Ability: When heated, tapioca starch can gel, making it useful in various baking and cooking applications, especially in gluten-free recipes.
Gluten-Free and Allergen-Free: Tapioca starch is naturally gluten-free and allergen-free, making it a safe choice for those with dietary restrictions.
Applications in the Food Industry
Tapioca starch’s chemical properties make it a versatile ingredient in the food industry. It is used for:
Thickening Sauces and Soups: Tapioca starch’s high viscosity makes it an excellent thickening agent for a variety of culinary creations.
Gluten-Free Baking: It is a key ingredient in gluten-free recipes, lending texture to baked goods.
Puddings and Desserts: Tapioca pudding, a classic dessert, relies on tapioca starch for its unique texture.
Beyond the Kitchen
Tapioca starch isn’t confined to cooking; it plays a significant role in various non-food industries. It’s used in the manufacturing of paper, textiles, and adhesives, among other applications.
Conclusion
Tapioca starch, with its intriguing chemistry and remarkable versatility, is more than just a thickening agent in the culinary world. It’s a testament to the power of natural ingredients and their transformative potential in diverse industries, offering a perfect blend of science and practicality. If you are interested in Tapioca Starch products for your specific business needs, please do not hesitate to contact us. Our team is ready to assist you in navigating these developments and finding the best solutions for your requirements.